几种常见的激活函数
激活函数在神经网络中起到了重要的作用,如果没有激活函数,层数再多的网络也只是线性模型,很可能无法正确地对复杂模式进行学习。
激活函数作用于每一层节点的输出之后,通过引入激活函数,网络具有了非线性关系的能力,从而获得更好的特征表达。接下来,介绍几种常见的激活函数:
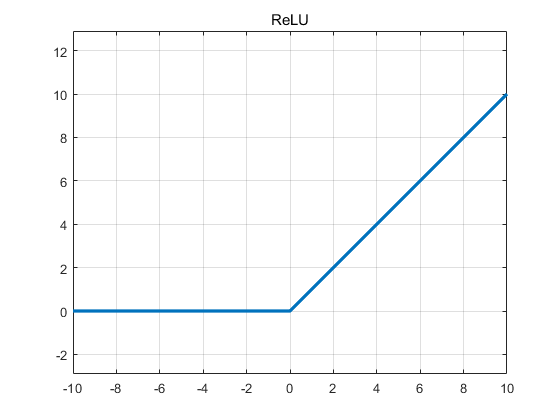
ReLU
def relu(x):
return max(x, 0)
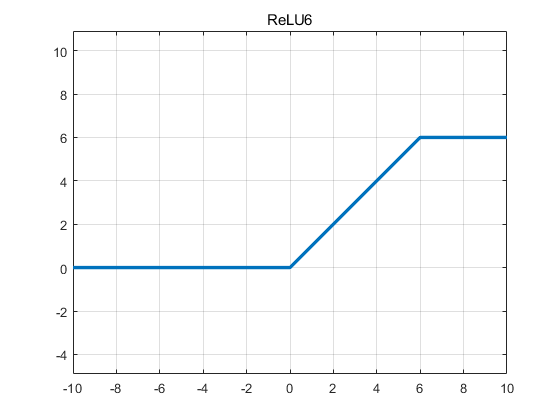
ReLU6
这里为什么是6,而不是其它数字,其实是经过实验验证得来的,取6通常可以得到最好的结果。
def relu6(x):
return min(max(x, 0), 6)
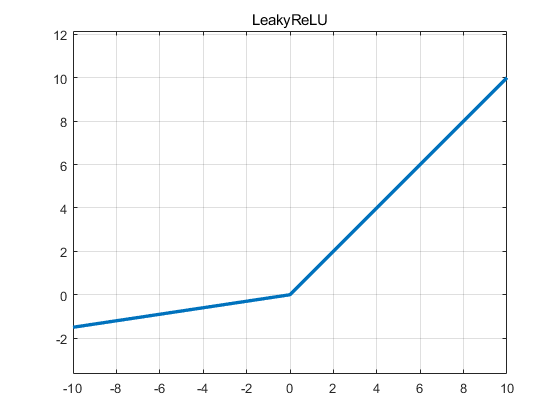
LeakyReLU
def leakyRelu(x, a):
# variable 'a' is a fixed coefficient
return max(x, a * x)
# more efficient implementation
def leakyRelu(x, a, name="lrelu"):
with tf.variable_scope(name):
f1 = 0.5 * (1 + a)
f2 = 0.5 * (1 - a)
return f1 * x + f2 * abs(x)
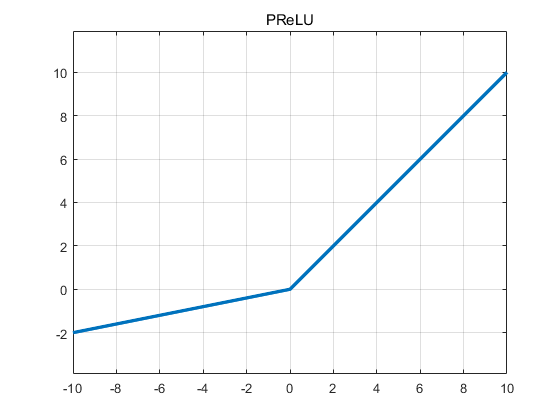
PReLU
相较于LeakyReLU,PReLU的系数是可以变化的,出自这篇文章Delving Deep into Rectifiers : Surpassing Human-Level Performance on ImageNet Classification,回头看看。
def prelu(_x, name):
# variable 'a' is learnable
_alpha = tf.get_variable(name + "prelu",
shape=_x.get_shape()[-1],
dtype=_x.dtype,
initializer=tf.constant_initializer(0.1))
pos = tf.nn.relu(_x)
neg = _alpha * (_x - tf.abs(_x)) * 0.5
return pos + neg
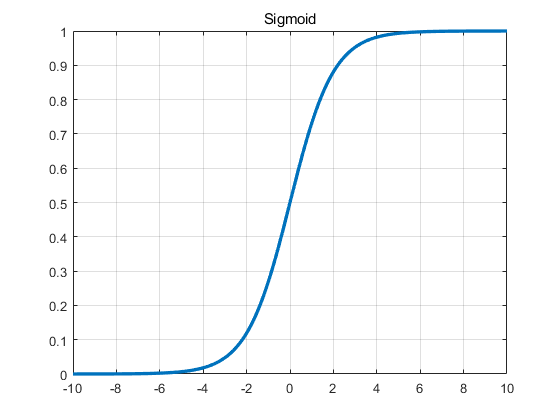
Sigmoid
def sigmoid(x):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
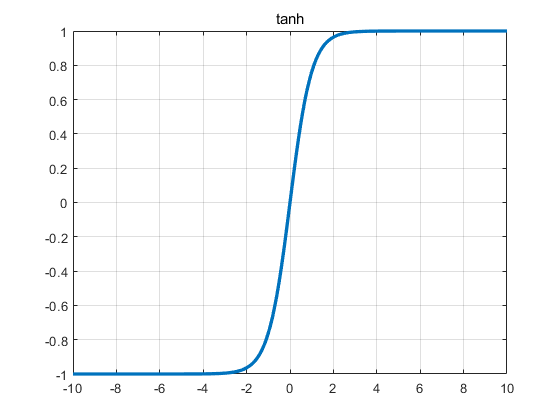
tanh
def tanh(x):
return (1 - np.exp(-2 * x)) / (1 + np.exp(-2 * x))